Pediatric Ophthalmology
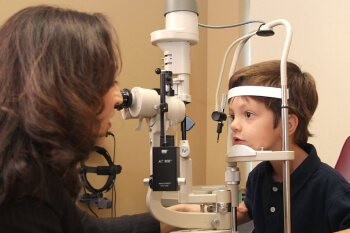
Vision develops in the brain until about age 9 years and can be affected by eyes that are not straight or do not focus correctly. A child can grow up with good vision in each eye if these problems are caught early, treated and maintained.
All ophthalmologists have training in children’s eye problems, but the pediatric ophthalmologist has had additional training and practice in examining children and caring for their eye problems. If your primary care doctor suggests that your child have his or her eyes checked, a pediatric ophthalmologist will have the greatest knowledge of the possible conditions and the greatest experience in examining children effectively.
What types of examinations do pediatric ophthalmologists provide?
- Vision testing- it takes particular skill to assess a child’s vision, particularly before the child is in school. Different methods have to be used at different ages.
- Measuring eye position in all patients who have misaligned eyes (strabismus)
- Examining the eye for abnormal structures, parts of the eye that are not functioning, signs that diseases are affecting theeyes such as genetic conditions, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, and diabetes, and injuries.
- Examinations of uncooperative, very young children, including premature babies.
- Determine what type and strength glasses a child needs at any age, by measuring the focusing ability of the eye (retinoscopy) after drops have made the pupils larger.
What kinds of treatments do pediatric ophthalmologists provide?
Medical treatments:
- Amblyopia (undeveloped vision or the vision part of a lazy eye) including glasses, patching, and dilating drops.
- Glasses prescriptions for simple lack of focus such as nearsightedness, astigmatism or farsightedness. Some fit contact lenses as well.
- Infection such as conjunctivitis, corneal ulcers and the tissue around the eye (orbit).
- Inflammation inside the eye (iritis) from arthritis conditions and injuries
- Glaucoma, high pressure in the eye, is treated by some pediatric ophthalmologists.
Surgery:
- Eye muscle surgery for misaligned eyes in patients of any age.
- Blocked tear ducts
- Cataract surgery in children
- Repair of injuries of the eye
Some do laser surgery in premature babies, glaucoma surgery, or droopy eye lid surgery (ptosis). This varies with the interest, training, and experience of the pediatric ophthalmologist.







